Question 1:
Match the columns in the following table and explain them.
Column 1
Column 2
Column 3
Farsightedness
Nearby object can be seen clearly
Bifocal lens
Presbyopia
Far away object can be seen clearly
Concave lens
Nearsightedness
Problem of old age
Concave lens
Column 1
|
Column 2
|
Column 3
|
Farsightedness
|
Nearby object can be seen clearly
|
Bifocal lens
|
Presbyopia
|
Far away object can be seen clearly
|
Concave lens
|
Nearsightedness
|
Problem of old age
|
Concave lens
|
ANSWER:
Column 1
Column 2
Column 3
Farsightedness
Far away object can be seen clearly
Convex lens
Presbyopia
Problem of old age
Bifocal lens
Nearsightedness
Nearby object can be seen clearly
Concave lens
Farsightedness: This defect is also known as Hypermetropia. It is an eye defect in which a person is unable to see nearby objects clearly but can see the far away objects clearly.
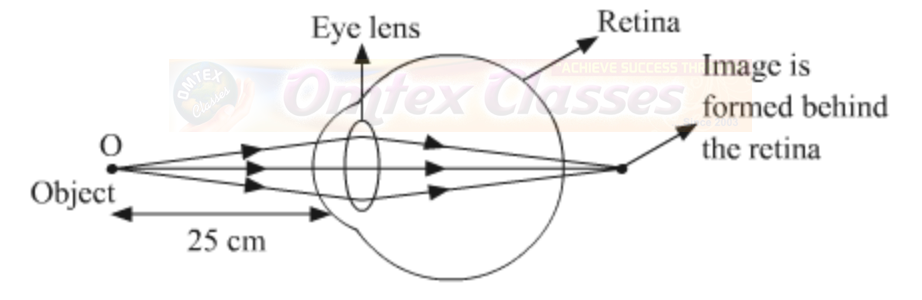 It is caused due to
1. reduction in the curvature of the lens
2. decrease in the size of the eyeball
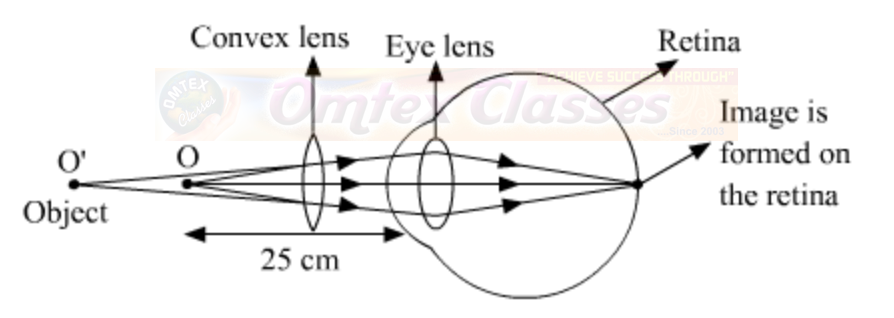
Since a convex lens has the ability to converge incoming rays, it can be used to correct this defect of vision, as you already have seen in the animation. The ray diagram for the corrective measure for a hypermetropic eye is shown in the given figure.
It is caused due to
1. reduction in the curvature of the lens
2. decrease in the size of the eyeball
Since a convex lens has the ability to converge incoming rays, it can be used to correct this defect of vision, as you already have seen in the animation. The ray diagram for the corrective measure for a hypermetropic eye is shown in the given figure.
Nearsightedness: This defect is also known as Myopia. It is a defect of vision in which a person clearly sees all the nearby objects, but is unable to see distant objects comfortably and his eye is known as a myopic eye. A myopic eye has its far point nearer than infinity. It forms the image of a distant object in front of the retina as shown in the figure.

It is caused by
1. increase in curvature of the lens
2. increase in length of the eyeball
Since a concave lens has an ability to diverge incoming rays, it is used to correct this defect of vision. The image is allowed to form at the retina by using a concave lens of suitable power as shown in the given figure.
 Presbyopia: This is a common defect of vision, which generally occurs at old age. A person suffering from this type of defect of vision cannot see nearby objects clearly and distinctly. A presbyopic eye has its near point greater than 25 cm and it gradually increases as the eye becomes older.
Presbyopia: This is a common defect of vision, which generally occurs at old age. A person suffering from this type of defect of vision cannot see nearby objects clearly and distinctly. A presbyopic eye has its near point greater than 25 cm and it gradually increases as the eye becomes older.
Presbyopia is caused by the
1. weakening of the ciliary muscles
2. reduction in the flexibility of the eye lens
It can be corrected using bifocal lens.
Column 1
|
Column 2
|
Column 3
|
Farsightedness
|
Far away object can be seen clearly
|
Convex lens
|
Presbyopia
|
Problem of old age
|
Bifocal lens
|
Nearsightedness
|
Nearby object can be seen clearly
|
Concave lens
|
Question 2:
Draw a figure explaining various terms related to a lens.
ANSWER:
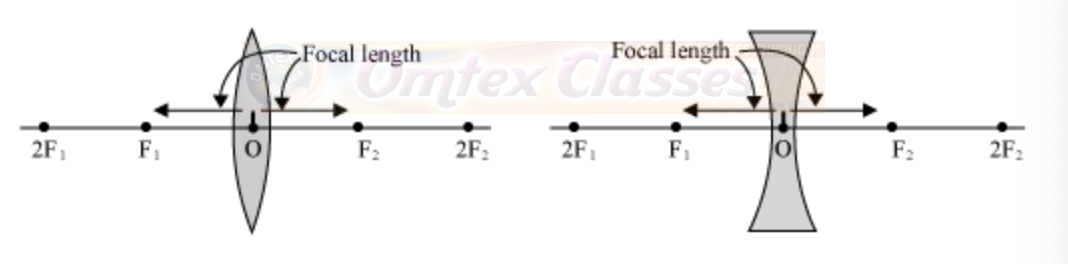
Terms Associated with Lenses:
Optical centre
Optical centre is a point at the centre of the lens. It always lies inside the lens and not on the surface. It is denoted by ‘O’.

Centre of curvature
It is the centre point of arcs of the two spheres from which the given spherical lens (concave or convex) is made. Since a lens constitutes two spherical surfaces, it has two centers of curvature.

Radius of curvature
The distance of the optical centre from either of the centres of curvatures is termed as the radius of curvature.
Principal axis
The imaginary straight line joining the two centers of curvature and the optical centre (O) is called the principal axis of the lens.

Focus
The focus (F) is the point on the principal axis of a lens where all incident parallel rays after refraction from the lens meet or appear to diverge from. For lenses there are two foci (F1 and F2) depending on the direction of incident rays.


Focal length
The distance between the focus (F1 or F2) and the optical centre (O) is known as the focal length of the lens.
Question 3:
At which position will you keep an object in front of a convex lens so as to get a real image of the same size as the object? Draw a figure.
Answer:
When an object is placed at the centre of curvature 2F1 of a convex lens, we will get a real image of the same size as the object.

Question 4:
Give scientific reasons:
a. Simple microscope is used for watch repairs.
ANSWER:
Simple microscope has convex lens which has the ability to produce 20 times larger as well as erect image of an object. This means the magnifying power of the microscope is very high. Thus, simple microscopes are used by watchmakers to see the small parts and screws of the watch while repairing it.
b. One can sense colours only in bright light.
ANSWER:
The cells present on the retina and responsible for colour vision are known as cone cells. These cells become active only under bright light and remain inactive under dark. Thus, we are able to sense only in bright light.
c. We cannot clearly see an object kept at a distance less than 25 cm from the eye.
ANSWER:
We cannot clearly see an object kept at a distance less than 25 cm from the eye. This is because the ciliary muscles of our eyes are unable to contract beyond certain limit. If the object is placed at a distance less than 25 cm from the eye, then the object appears blurred because light rays coming from the object meet behind the retina.
Question 5:
Explain the workings of an astronomical telescope using refraction of light.
ANSWER:
The astronomical telescope consists of two lenses: objective and eyepiece. Objective has larger focal length and diameter to accommodate the maximum amount of light coming from the far away (astronomical) objects. A parallel beam of rays from an astronomical object is made to fall on the objective lens of the telescope. It forms a real, inverted and diminished image A'B' of the object. The eyepiece is so adjusted that A'B' lies just at the focus of the eye piece. Therefore, a highly magnified image of the object is formed at infinity. The same has been shown in the figure below.

Question 6:
Distinguish between:
a. Farsightedness and Nearsightedness
b. Concave lens and Convex lens
ANSWER:
a. Farsightedness and Nearsightedness
Farsightedness
Nearsightedness
In this defect, person clearly sees all the far away objects, but is unable to see the nearby objects comfortably and clearly.
In this defect, person clearly sees all the nearby objects, but is unable to see distant objects comfortably and clearly.
It is caused due to decrease in curvature of the eye lens or decrease in length of eyeball.
It is caused due to increase in curvature of the eye lens or increase in length of eyeball.
In this defect, image is formed behind the retina.

In this defect, image is formed in front of the retina.

It is corrected using a convex lens.
It is corrected by using concave lens.
b. Concave lens and Convex lens
Concave lens
Convex lens
It is a diverging lens because it diverges the rays falling on it.
It is a converging lens because it converges the rays falling on it.
It is thin at the center and bulged at the edge.
It is thin at the edge and bulged at the centre.
The image formed by concave lens is always diminished and virtual.
The image formed by convex lens can be real as well as virtual. Also, the image formed can be diminished as well as magnified.
It has a virtual focus.
It has a real focus.
Farsightedness
|
Nearsightedness
|
In this defect, person clearly sees all the far away objects, but is unable to see the nearby objects comfortably and clearly.
|
In this defect, person clearly sees all the nearby objects, but is unable to see distant objects comfortably and clearly.
|
It is caused due to decrease in curvature of the eye lens or decrease in length of eyeball.
|
It is caused due to increase in curvature of the eye lens or increase in length of eyeball.
|
In this defect, image is formed behind the retina.
|
In this defect, image is formed in front of the retina.
|
It is corrected using a convex lens.
|
It is corrected by using concave lens.
|
Concave lens
|
Convex lens
|
It is a diverging lens because it diverges the rays falling on it.
|
It is a converging lens because it converges the rays falling on it.
|
It is thin at the center and bulged at the edge.
|
It is thin at the edge and bulged at the centre.
|
The image formed by concave lens is always diminished and virtual.
|
The image formed by convex lens can be real as well as virtual. Also, the image formed can be diminished as well as magnified.
|
It has a virtual focus.
|
It has a real focus.
|